

Computational simulations are a powerful approach to addressing one of the "Grand Challenges in the Chemical Sciences", namely the ability to understand and control the properties of complex macromolecular systems. In turn, one of the great challenges for computational simulations is to sample the conformational space of complex macromolecular systems sufficiently to enable reliable predictions to be made. The ExTASY project involves the development of a set of software tools that, by coupling large ensemble Molecular Dynamics calculations with novel analysis methods and efficient integrators, can provide orders-of-magnitude improvements in sampling in comparison to standard approaches. ExTASY tools are designed to be flexible (able to be applied to many different types of simulation problem) and extensible (able to be integrated with many other simulation software tools)
We have developed a range of Open Source software tools and libraries for advanced sampling with MD.
Descriptions of each, along with links to documentation and instruction on how to obtain the software are given.
Each component of the ExTASY toolkit may be used separately or combined to build advanced sampling workflows
ExTASY works at the intersection of Biomolecular Science, Mathematics and Computer Science. Browse our list of publications related to the ExTASY project.
Tutorial: Tools for Advanced Sampling of Macromolecular Systems - Programme and registration
Details of past and upcoming events related to the project can be found here
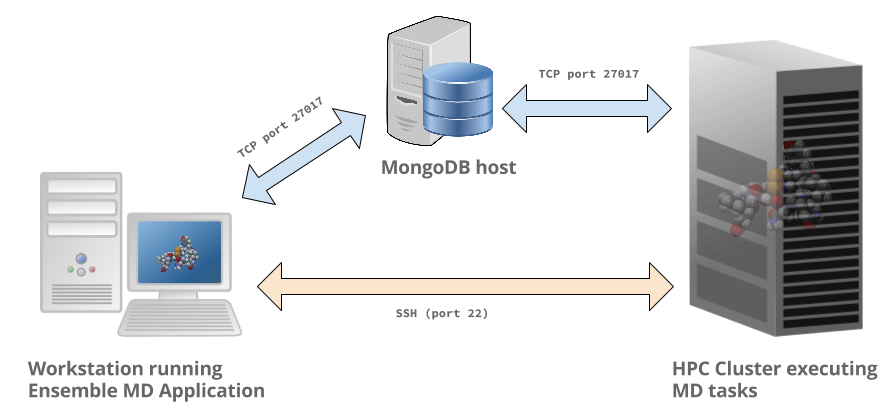
Running sampling applications on remote HPC systems using Ensemble MD.
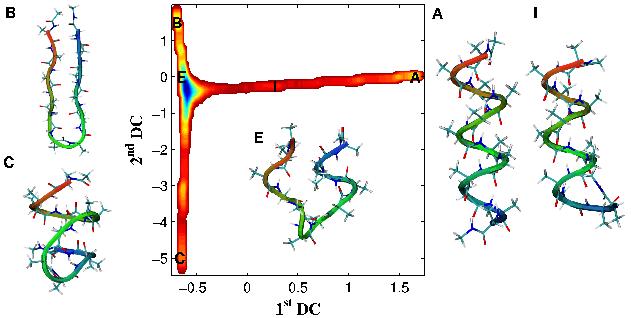
Free energy landscape of Alanine-12, computed using Diffusion Map-directed-MD.